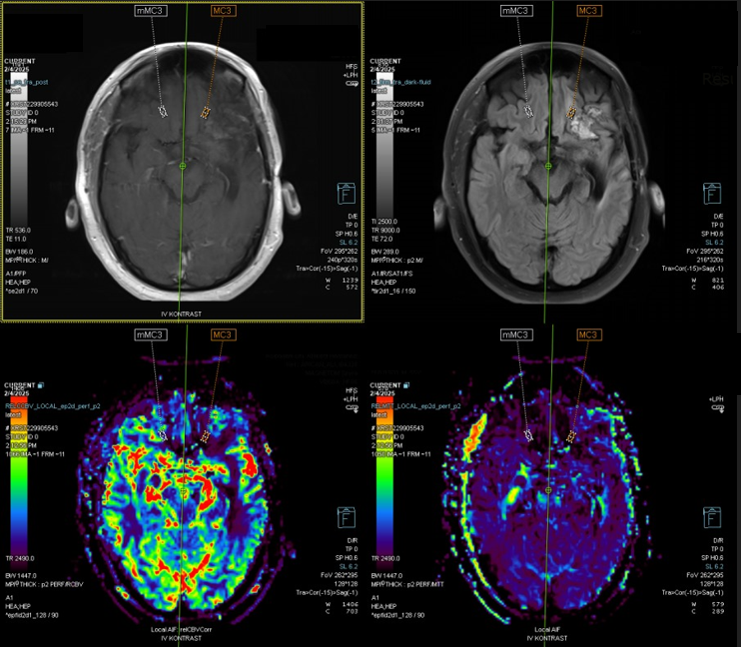
Perfusion MRI is an advanced imaging technique that measures cerebral blood flow (CBF), providing critical information about the blood supply to brain tissues. It evaluates the circulation dynamics, especially the flow of oxygenated blood through the cerebral vasculature, and identifies areas with compromised perfusion.
Applications
1.Assessing Cerebral Blood Flow in Neurological Conditions:
- Stroke & Ischemia: Perfusion MRI plays a crucial role in identifying hypoperfused regions in conditions like ischemic stroke, where parts of the brain are at risk of infarction. It helps delineate the ischemic penumbra (brain tissue at risk but still salvageable) from the core infarct (irreversibly damaged tissue).
- Brain Tumors: MRI perfusion is valuable in assessing tumor vascularity, particularly in malignant tumors like glioblastomas, which exhibit high blood flow. This helps distinguish aggressive tumors from benign lesions and aids in surgical planning.
2.Postoperative Monitoring:
- Tumor Recurrence vs. Radiation Necrosis: One of the key applications of brain Perfusion MRI in the postoperative period is differentiating tumor recurrence from radiation necrosis following radiotherapy. Tumor recurrence typically presents with increased perfusion due to the angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation) associated with tumor growth. In contrast, radiation necrosis often shows low perfusion due to damaged blood vessels. Perfusion MRI can help distinguish these two conditions, guiding clinical decision-making and further treatment interventions.
- Viability of Brain Tissue: After tumor resection or stroke-related surgery, Perfusion MRI helps assess the viability of brain tissue, particularly in areas that were previously ischemic or near the surgical site. It indicates whether normal blood flow has been restored or if there are regions of ongoing ischemia that require further attention.
Perfusion MRI © ENI
Advantages in Neurosurgery
1.Surgical Planning:
MRI perfusion brain, helps identify areas with compromised blood flow that need special attention during surgery. This is particularly important in brain tumor resections, radiation necrosis surgeries and stroke surgeries, where preserving healthy brain tissue is crucial.
2.Postoperative Follow-Up:
Non-invasive and efficient, perfusion MRI brain, allows for ongoing monitoring of brain perfusion in the postoperative period. It is invaluable for detecting early tumor recurrence or identifying regions of ischemic injury that might need additional interventions.
