In neurosurgery, precision and accuracy are paramount. The O-Arm CT system is an advanced, intraoperative imaging tool that is revolutionizing the way complex spinal surgeries are performed. It provides real-time, high-resolution, three-dimensional imaging during surgery, enabling neurosurgeons to make precise decisions and achieve optimal outcomes for their patients. This mobile, multi-dimensional imaging system is increasingly used in the operating room (OR) for spinal surgeries and some critical neurosurgical procedures.
Role of O-Arm CT in Neurosurgery
The O-Arm CT plays a crucial role in improving the safety and efficacy of neurosurgical procedures. Traditional imaging methods, such as preoperative CT or MRI scans, provide static images of the patient’s anatomy. However, these images can quickly become outdated once the surgery begins. The O-arm navigation system, provides real-time intraoperative imaging, allowing surgeons to visualize the surgical site in three dimensions while performing the procedure.
- Real-Time Imaging: O arm navigation, provides immediate feedback on the position and orientation of surgical instruments, as well as the status of the spinal cord structures. This is particularly important during critical procedures such as tumor resections, spinal fusion, and spinal deformity correction, where precision is essential.
- Improved Surgical Precision: The ability to obtain high-resolution images during surgery allows surgeons to confirm the accuracy of their actions. For example, in spinal surgery, O-arm navigation enables the surgeon to verify the correct placement of screws and other implants, minimizing the risk of misplacement and improving the likelihood of successful outcomes.
- Minimizing Risk of Complications: The O-Arm CT helps ensure the identification of any potential complications during surgery, such as bleeding, anatomical misalignments, or unintended injury to critical structures. Real-time imaging helps ensure that corrective measures can be taken immediately, reducing the chances of postoperative complications such as nerve damage or infection.
- Guidance for Minimally Invasive Surgeries: For minimally invasive neurosurgical techniques, the O-Arm CT helps ensure navigation through small incisions with high precision. This helps ensure that surgeons can achieve the intended outcomes without causing excessive damage to surrounding tissues, thereby promoting faster recovery and reducing postoperative pain.
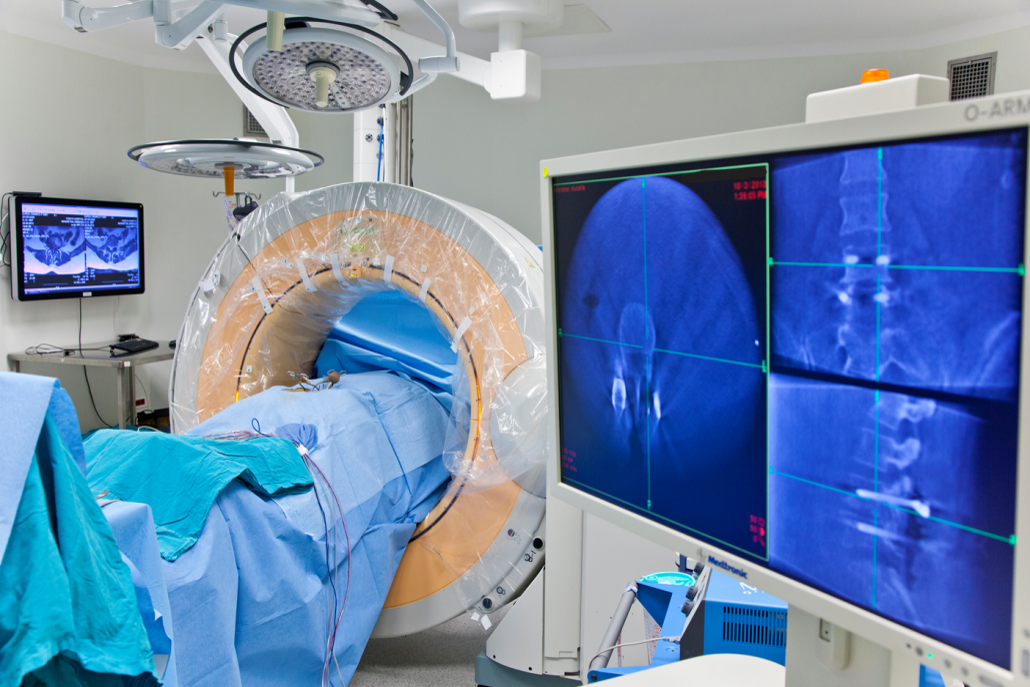
O-Arm CT © ENI
How O-Arm CT Works
The O-Arm CT system consists of a large, O-shaped apparatus that surrounds the patient while rotating 360 degrees to capture multiple images during surgery. These images are then processed by advanced software to create high-resolution 2D and 3D images that can be viewed by the surgical team on a computer screen.
The system operates in the following steps:
- Positioning and Setup:
- The patient is positioned on the operating table, and the O-Arm CT is aligned around the surgical area.
- Markers or reference points are often placed on the patient’s skin to ensure that the images are correctly aligned with the surgical site.
- Image Acquisition:
- The O-Arm CT system rotates around the patient, capturing continuous images from multiple angles.
- These images are transmitted to the connected computer system, where they are processed to generate detailed 3D models of the patient’s anatomy.
- Real-Time Imaging:
- The processed images are displayed on monitors in the operating room, providing real-time feedback to the surgical team. Surgeons can use this data to guide their instruments and adjust their approach if needed.
- The system also allows for immediate imaging after specific steps in the surgery to verify the success of the procedure, such as confirming the correct placement of screws during spinal surgery or checking for any complications after a tumor resection.
- Intraoperative Navigation and Verification:
- In many cases, O-Arm CT is integrated with navigation systems that provide precise guidance based on the real-time images. This helps ensure that surgical instruments are correctly positioned relative to the patient’s anatomy, significantly reducing the risk of error.
- The system can also be used to verify the positioning of implants or other surgical components during the procedure.
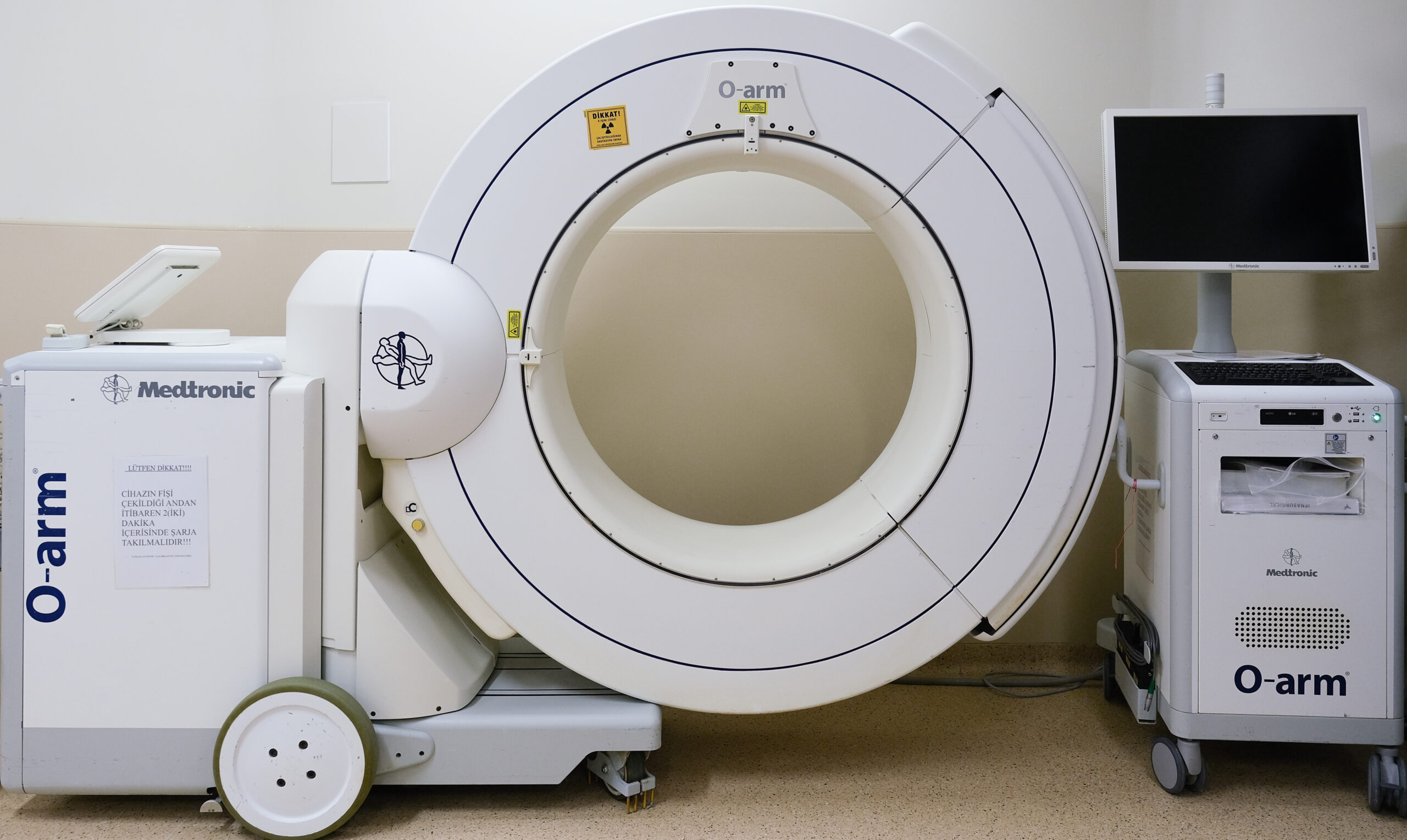
O-Arm CT © ENI
Advantages of O-Arm CT in Neurosurgery
- Enhanced Surgical Accuracy: O-Arm CT provides detailed images of the surgical site in real-time, allowing neurosurgeons to verify and adjust their actions for maximum precision, leading to better surgical outcomes and fewer complications.
- Minimizing Risk of Complications: By offering up-to-date imaging, the O-Arm CT helps ensure that surgical errors are minimized. For example, in spinal surgery, it helps ensure that screws and other implants are placed in the correct anatomical location, helping to prevent malposition and the need for revision surgeries.
- Faster Recovery and Less Postoperative Pain: The precision offered by O-Arm CT contributes to less invasive procedures, which generally result in smaller incisions, faster recovery times for patients. In turn, patients experience less postoperative pain and a quicker return to daily activities.
- Support for Complex Procedures: In complex neurosurgical cases, such as spinal deformity corrections, the O-Arm CT helps ensure accurate visualization of hard-to-reach areas, aiding in confirming that the surgical approach is precise, minimizing risks, and improving success rates.
- Efficient Use of Time and Resources: By providing intraoperative imaging, the O-Arm CT helps ensure that the need for multiple preoperative imaging studies or additional postoperative scans is reduced, ultimately saving valuable time in the operating room and improving resource utilization.
- Real-time Correction: The O-Arm CT system helps ensure real-time correction during surgery. This allows the surgeon to make immediate adjustments based on the most up-to-date imaging, ensuring optimal placement of surgical instruments and implants, reducing errors, and enhancing overall surgical precision.
