Neuroendoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to examine and treat part of the central nervous system, such as the brain and spinal cord. During this procedure, an endoscope—a thin, flexible or rigid tube equipped with a camera and light source—is inserted into the body through small incisions, providing video imaging. This allows the surgeon to visualize and intervene in the structures of the nervous system in great detail without the need for large incisions.
In the field of neurosurgery, neuroendoscopy surgery has become a critical tool across a wide range of procedures, including surgeries related to the brain, skull base, spinal cord, and, more recently, peripheral nerve surgeries. This technique offers substantial benefits, particularly for conditions involving deep, hard-to-reach areas such as the skull base, as well as for the treatment of hydrocephalus and other complex brain surgeries.
Applications of Neuroendoscopy
Neuroendoscopy has expanded its applications significantly in recent years, covering a broad spectrum of clinical indications. Some of the key areas where neuroendoscopy is commonly used include:
- Lesions at the skull base
- Pituitary adenomas
- Solid intraventricular tumors
- Hydrocephalus treatment via Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV)
- Brain cysts (arachoid cyst, colloid cyst, etc.)
- Sinus base surgery
- Craniopharyngiomas
- Lesions located in deep brain structures
- Hypothalamic hamartomas
- Intracerebral hematomas
- Vascular pathologies
- Craniosynostosis
- Spinal pathologies
- Carpal tunnel
- Lumbar disc herniation
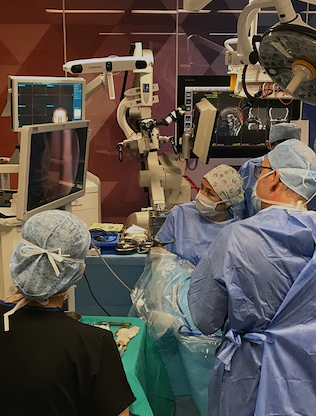
Neuroendoscopy © ENI
Advantages of Neuroendoscopy in Neurosurgery
Neuroendoscopy provides several key benefits in neurosurgical practice, primarily due to its minimally invasive nature. The main advantages include:
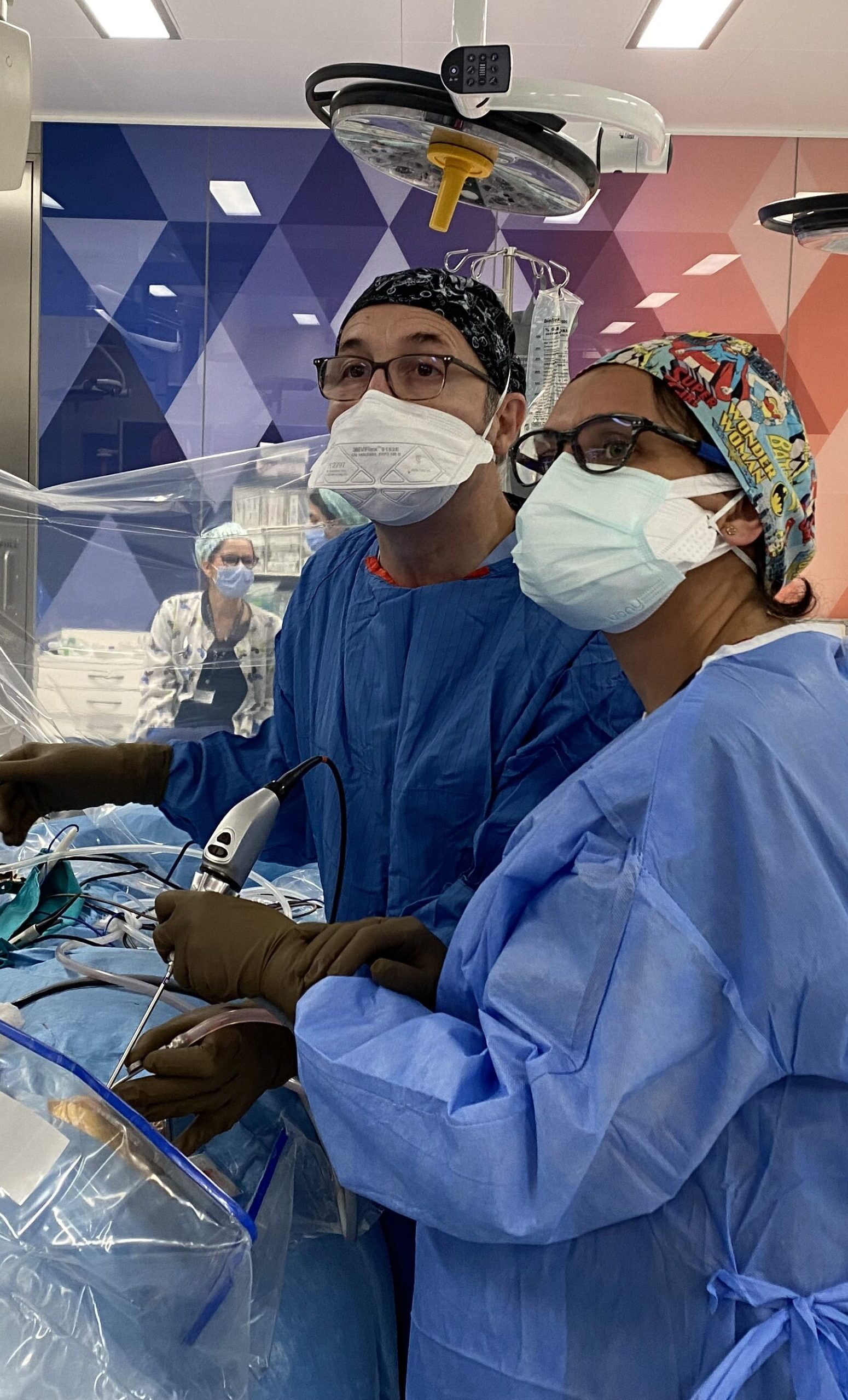
Neuroendoscopy © ENI
- Minimally invasive approach: Compared to traditional open surgery, neuroendoscopic procedures are performed through significantly smaller incisions. This results in faster recovery times, shorter hospital stays, and reduced levels of post-operative pain.
- Real-Time imaging and high resolution: The high-resolution images provided by the endoscope allow surgeons to clearly visualize the structure of tissues, tumors, or abnormalities during the procedure. This enables more precise and accurate interventions.
- Access to larger areas through smaller incisions: Endoscopes offer the ability to access large, difficult-to-reach anatomical areas with minimal incisions. This is particularly beneficial for accessing deep brain structures and the spinal cord, which are often challenging to approach with traditional methods.
- Facilitating repeated procedures: Neuroendoscopic surgery is less traumatic, making it easier to perform multiple interventions when needed, especially in cases of recurrent conditions such as craniopharyngiomas. This reduces the overall risk and trauma for the patient during repeated surgeries.
Neuroendoscopically assisted microsurgery
Endoscopes can be used as auxiliary tools in microsurgery, particularly in operations for cerebrovascular aneurysms, microvascular decompression, and lesions of the cerebellopontine angle. Endoscopes of different designs are available for different uses. They provide the important ability to look around corners or behind the lesion in question. In aneurysm surgery, for example, the optimal position of the clip can be confirmed, while in microvascular decompression the vascular loop impinging on the trigeminal nerve can be inspected from all sides.
Neuroendoscopy helps in the total removal of the tumor by seeing the areas where the microscope is insufficient in tumor surgery.
