Laser energy is a method used in neurosurgery, particularly for brain tumors, epilepsy, radiation necrosis, brain metastasis and certain selected patient groups. Laser-Induced Thermal Therapy (LITT) relies on the principle of focusing high-energy laser beams on the target area to heat tissues and create the desired therapeutic effects.
Principles of the Procedure
The use of laser energy is based on the principle of focusing high levels of heat onto the targeted area, leading to the destruction of abnormal tissue masses.
- Placement of the Fiber Optic Catheter: The catheter that carries the laser energy is placed under general anesthesia in the operating room with a minimally invasive approach. A small incision is made in the head region to guide the catheter to the target tissue.
- Guidance with Imaging Techniques: The procedure is performed under real-time MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) guidance. MRI provides continuous visual monitoring to ensure the laser beam is accurately focused and reaches the target tissue.
- Heat Application and Tissue Destruction: Laser energy is directed to the targeted tissue, heating the area. This high heat causes abnormal cells to be damaged and killed, while surrounding healthy tissue is preserved.
- Continuous Monitoring: The temperature of the tissue being treated with laser energy is continuously monitored during the procedure. Additionally, surrounding tissues are also monitored in real-time using MRI, enabling the detection and prevention of any abnormal reactions or heat fluctuations.
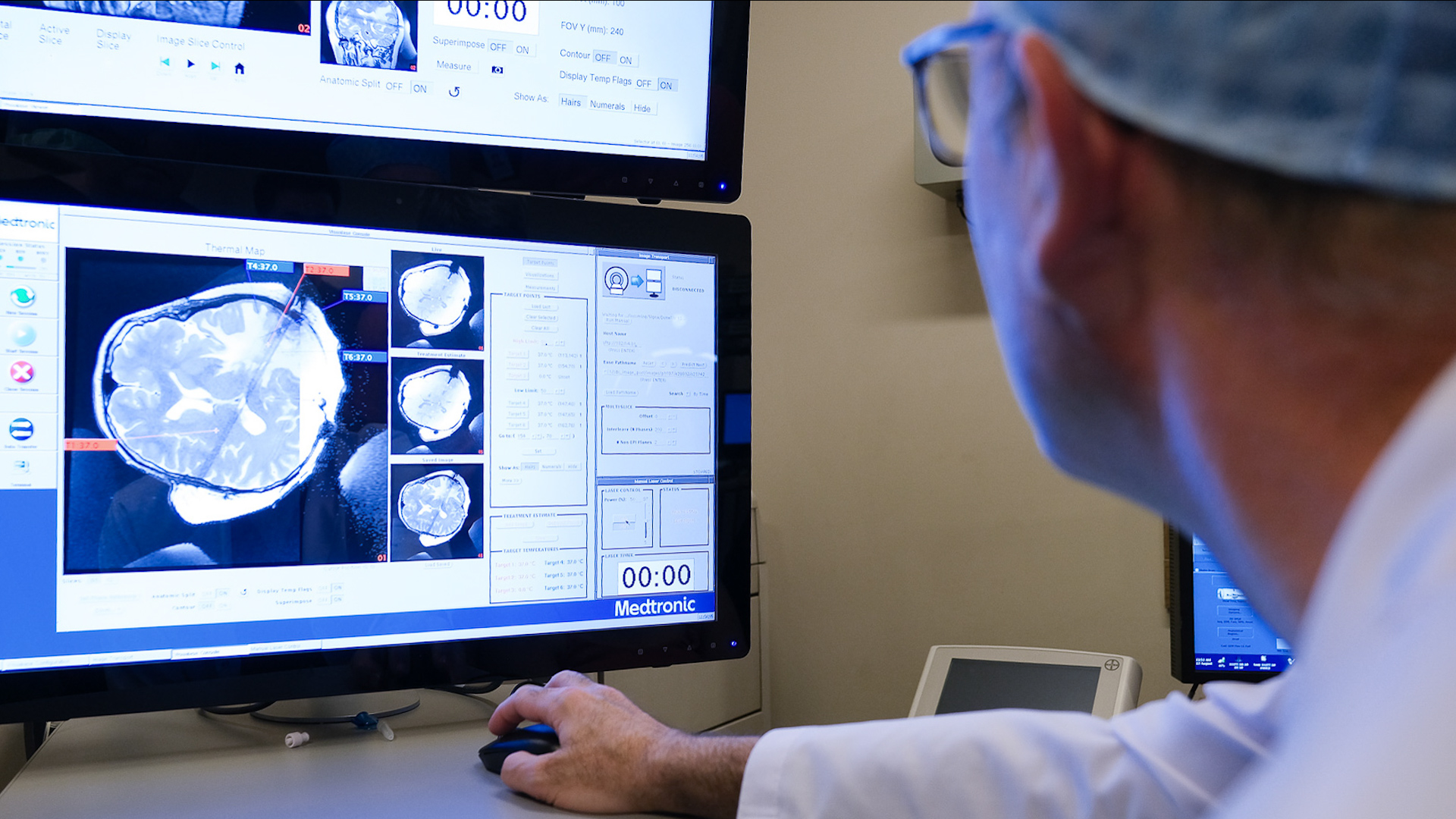
Laser Energy © ENI
Applications
- Brain Tumors: It is an effective treatment option for certain deep-seated brain tumors that are difficult to remove surgically.
- Metastasis: In the treatment of cancer that has metastasized to the brain, laser energy helps to destroy cancerous cells.
- Epilepsy Treatment: In cases of epilepsy that do not respond to medical treatment, laser energy is used to destroy abnormal brain areas responsible for seizures.
- Radiation Necrosis: After radiation therapy for brain tumors, normal brain tissue may be damaged and necrosis (dead tissue) can occur. This condition is known as radiation necrosis. Laser energy helps to target the abnormal tissue in the necrotic area, preserving surrounding healthy tissue and aiding in the removal of damaged tissue.
Advantages of Laser Energy in Neurosurgery
- Minimally Invasive Intervention: Laser energy provides a much less invasive approach than traditional surgery. The fiber optic catheter is placed through a small 3.2 mm incision. This minimal invasive procedure reduces complication risks and accelerates the recovery process for patients.
- Short Recovery Time: Patients are typically hospitalized for one day post-procedure, with no need for intensive care in most cases. Additionally, postoperative pain levels are generally low.
- High Targeting Precision: With MRI guidance, laser energy allows surgeons to visualize the target area with high precision and accurately direct the laser beams. This helps ensure the protection of healthy tissue during treatment.
- Repeatable Treatment Options: The procedure can be repeated if necessary. If a tumor or lesion has not been completely eliminated, additional laser energy can be applied to continue the treatment.
- Blood-Brain Barrier: The region where laser energy is applied may temporarily disrupt the blood-brain barrier. This allows planned chemotherapy or biologic drug therapies to penetrate the brain more effectively after the procedure.
