MR Tractography (Magnetic Resonance Tractography) is a specialized imaging technique that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the white matter tracts in the brain, which are responsible for transmitting information between different regions of the brain. This technique provides a 3D map of the brain’s neural pathways—such as the corticospinal tract, corpus callosum, and optic radiation—by detecting the orientation and direction of water diffusion along the nerve fibers. This allows clinicians to see and track the fibers that make up these pathways in high detail, providing an understanding of how different regions of the brain communicate with each other.
Applications
1.Preoperative Planning for Tumor Resection:
- Mapping Critical Pathways: In cases of brain tumors, especially those located near or within critical brain regions (e.g., motor cortex, sensory areas, language centers), MRI Tractography plays a crucial role in preoperative planning. The technique helps identify the exact location of vital neural pathways that must be preserved to minimize the risk of postoperative deficits such as paralysis, sensory loss, or aphasia. This allows the surgeon to plan the tumor resection while avoiding damage to essential white matter tracts.
- Tumor–Tract Relationship: By visualizing how a tumor interacts with surrounding neural tracts, MR Tractography helps determine whether it is infiltrating or displacing important pathways. This information guides decisions about the extent of tumor removal and whether additional approaches, such as stereotactic radiosurgery, are necessary to treat the tumor without affecting critical brain functions.
2.Surgical Planning for Vascular Malformations and Aneurysms:
- Preserving Vascular and Neural Structures: In surgeries involving brain vascular malformations (e.g., arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)) or aneurysms, MR Tractography is used to visualize the relationship between blood vessels and surrounding neural pathways. Understanding the proximity of critical tracts to vascular structures is essential to minimize the risk of ischemia or nerve damage during the procedure.
- Avoiding Critical Pathways: If a vascular malformation is located near major motor, sensory, or language pathways, MR Tractography allows the surgeon to navigate around these critical areas during the surgical approach, ensuring that the surgical intervention does not inadvertently damage important neural structures.
3.Spinal Cord Surgery:
- Mapping Spinal Pathways: MR Tractography can be applied in spinal cord surgeries to visualize the descending motor tracts and ascending sensory pathways, such as the corticospinal tract and dorsal column pathways. This is particularly useful in cases of spinal tumors, spinal stenosis, or spinal cord injury, where it is crucial to preserve motor function and sensory perception during surgery.
- Guiding Surgical Decisions: By providing a clear map of spinal pathways, MR Tractography helps surgeons avoid damaging critical neural structures during procedures like spinal decompression, tumor resection, or spinal fusion, ultimately reducing the risk of permanent motor deficits or sensory loss.
4.Functional Brain Mapping in Epilepsy Surgery:
- Identifying Epileptogenic Zones and Vital Pathways: In epilepsy surgery, particularly in cases of drug-resistant epilepsy, MRI with tractography helps map the brain’s functional networks by showing the relationship between epileptogenic zones (areas where seizures originate) and surrounding functional pathways. This is particularly important when dealing with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy or lesions near the motor cortex.
- Preserving Functional Networks: By visualizing the proximity of critical neural pathways to the epileptic focus, MR Tractography ensures that functional areas, such as the motor, sensory, and language areas, are preserved while removing the epileptogenic tissue, thus minimizing postoperative deficits.
5.Minimizing Risks in Complex Brain Surgeries:
- Neuroplasticity and Reorganization: MR Tractography can also help in understanding the neuroplasticity of the brain in patients undergoing resection or stimulation surgeries. By showing the intactness of critical neural tracts, it provides valuable insights into the brain’s ability to reorganize its functions, which is crucial in predicting postoperative recovery.
- Guiding Intraoperative Decisions: In some cases, MR Tractography can be used to guide intraoperative decisions. For example, in awake craniotomy procedures or neurosurgical interventions near functional areas, real-time tractography may be used in conjunction with other monitoring techniques (e.g., electrocorticography) to preserve motor or sensory functions during the procedure.
Advantages in Neurosurgery
1.Detailed Visualization of Neural Pathways:
MR Tractography offers a high-resolution, non-invasive method for visualizing the white matter tracts that are essential for brain function. This allows neurosurgeons to map complex neural networks with high precision, providing them with detailed anatomical information that is critical for planning surgeries around functional brain areas.
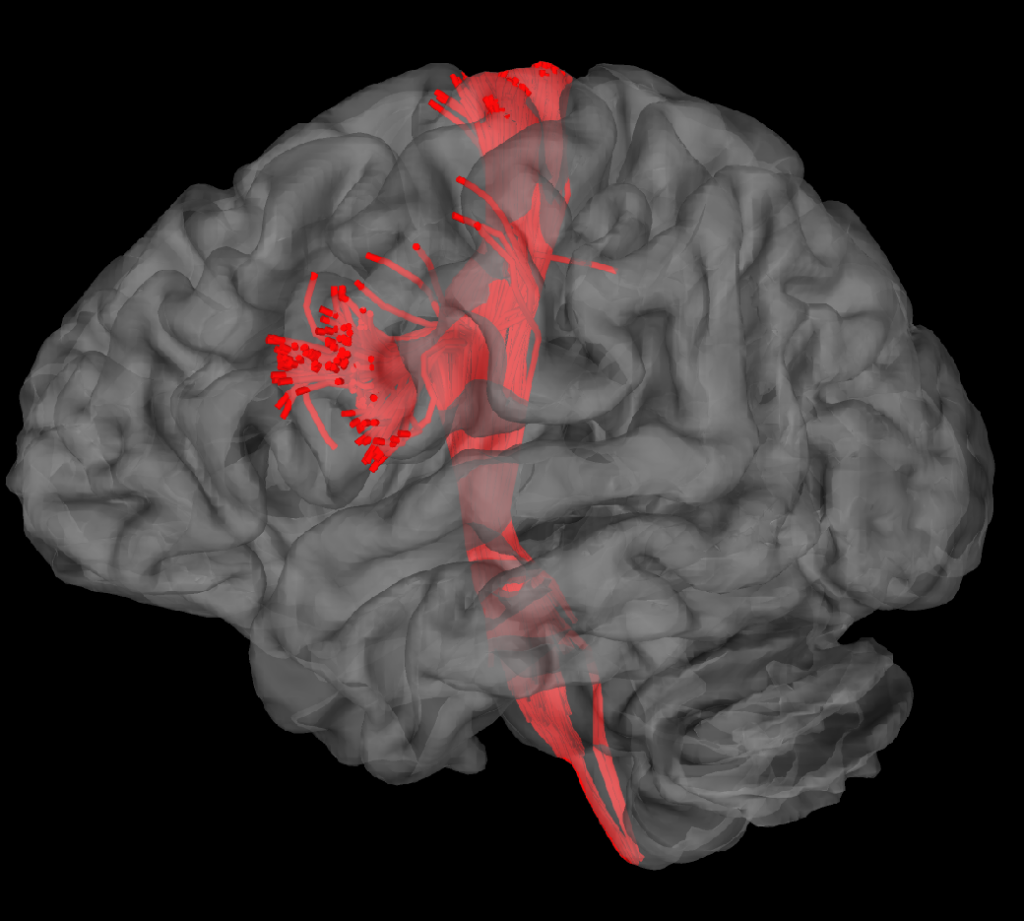
MR Tractography © ENI
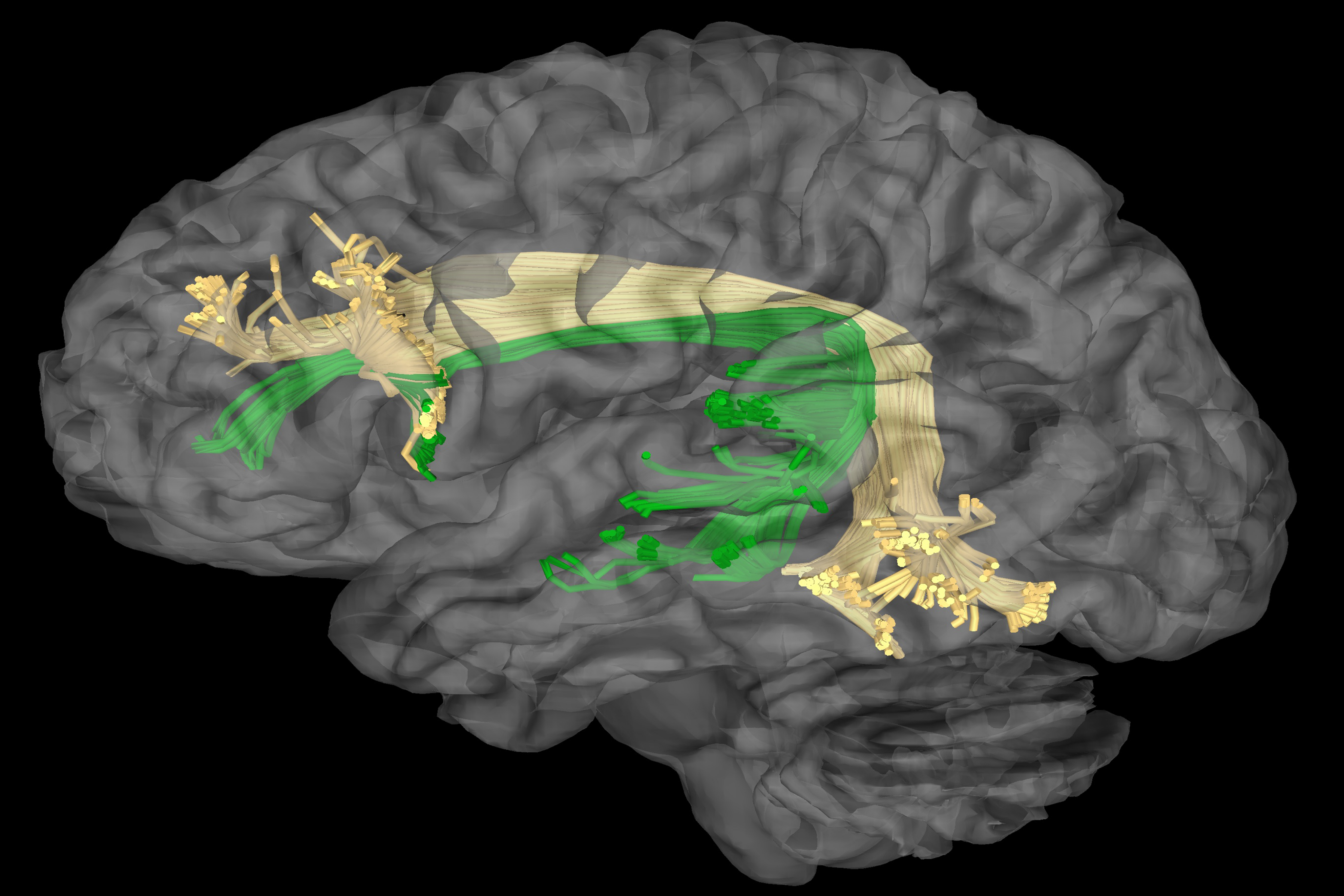
MR Tractography © ENI
2.Guiding Tumor Resection and Minimizing Functional Loss:
The primary advantage of MR Tractography in brain tumor resection is its ability to preserve critical neural tracts during surgery. By visualizing the relationship between tumors and surrounding neural pathways, the surgeon can plan an approach that minimizes the risk of functional impairment, such as motor weakness, speech difficulties, or sensory loss, even when the tumor is located close to these areas.
3.Enhanced Surgical Planning and Precision:
MR Tractography significantly enhances preoperative planning, providing a comprehensive map of the brain’s white matter. This 3D mapping helps the surgeon visualize the spatial relationship between tumors, vascular malformations, and important brain tracts, ultimately improving surgical precision and reducing the likelihood of inadvertent damage to critical structures.
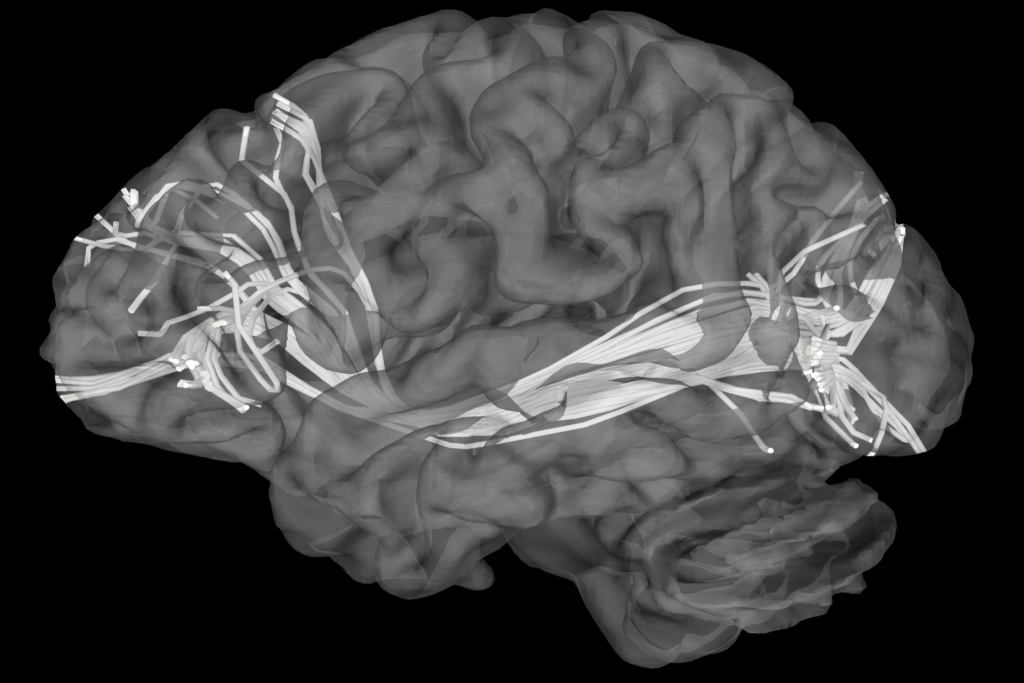
MR Tractography © ENI
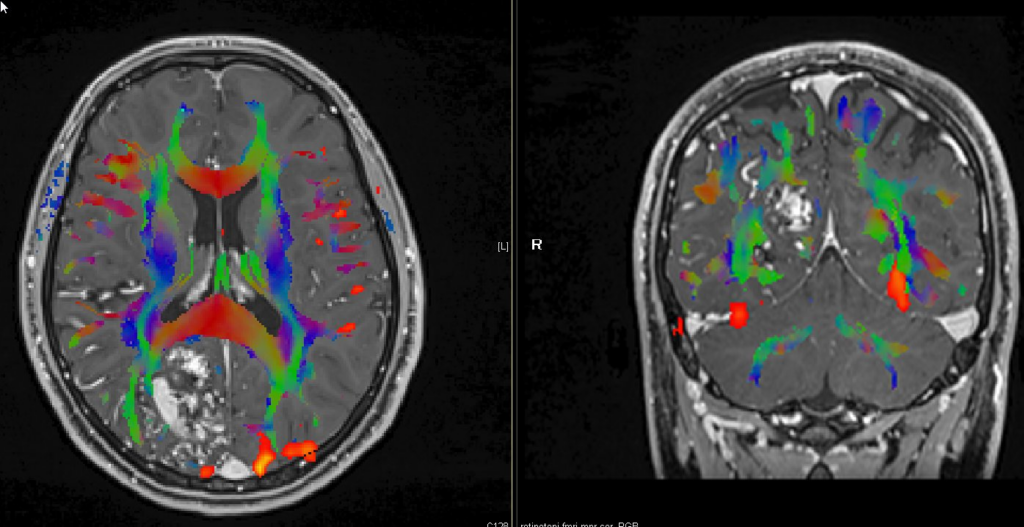
MR Tractography © ENI
4.Improved Patient Outcomes:
By accurately mapping neural pathways, MR Tractography helps to reduce the risk of neurological deficits in patients undergoing brain surgery. Whether in tumor resection, vascular malformation surgery, or epilepsy treatment, its use ensures that essential brain functions are preserved, leading to better postoperative recovery and quality of life.
5.Facilitating Minimally Invasive Approaches:
In minimally invasive or endoscopic surgeries, where direct access to the brain or spinal cord is limited, MR Tractography serves as a valuable tool for guiding the surgeon to avoid critical pathways. This is especially important in surgeries such as stereotactic radiosurgery, where real-time tract monitoring enhances the precision of the procedure and minimizes risks.
6.Reducing Surgical Risk in Complex Cases:
In highly complex cases, such as deep brain stimulation, spinal cord injury, or functional neurosurgery, MR Tractography allows the surgeon to assess the condition of critical neural tracts and make more informed decisions about how to approach the surgery safely, ultimately reducing surgical risk and improving patient outcomes.
